KNOWLEDGE BASE
- Details
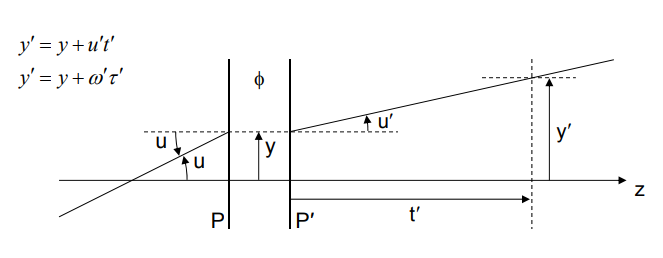
Paraxial ray tracing assumes that the tangent and sine of all angles are equal to the angles themselves (in other words, tan(u)=u and sin(u)=u ). This approximation is valid for small angles but can lead to the propagation of error as ray angles increase.
- Details
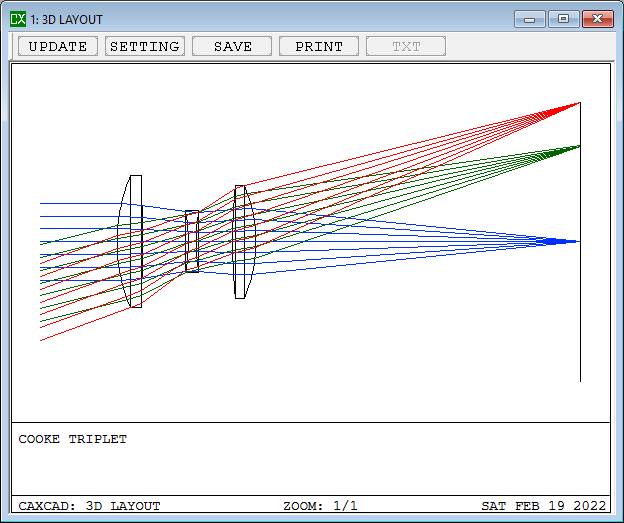
The Cooke triplet is a photographic lens designed and patented (patent number GB 22,607) in 1893 by Dennis Taylor who was employed as chief engineer by T. Cooke & Sons of York. It was the first lens system that allowed elimination of most of the optical distortion or aberration at the outer edge of lenses. The Cooke triplet is noted for being able to correct the Seidel aberrations.
- Details
A doublet is an optical lens assembly consisting of two individual lenses cemented or spaced closely together. The purpose of a doublet is to correct chromatic aberration, a common optical aberration that causes different wavelengths of light to focus at different distances from the lens, resulting in color fringing or blurring in images.
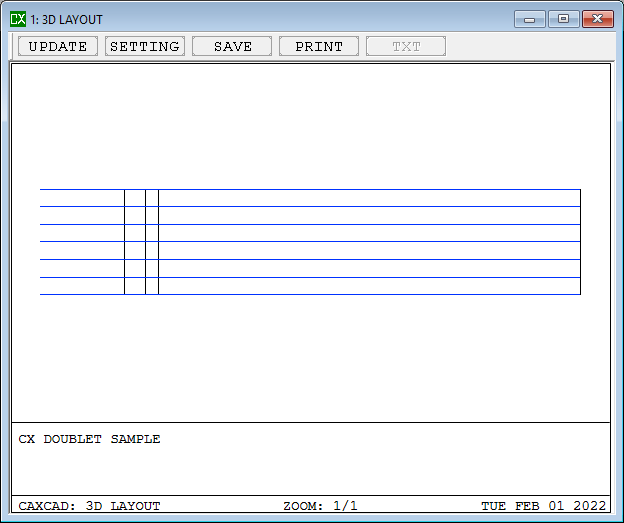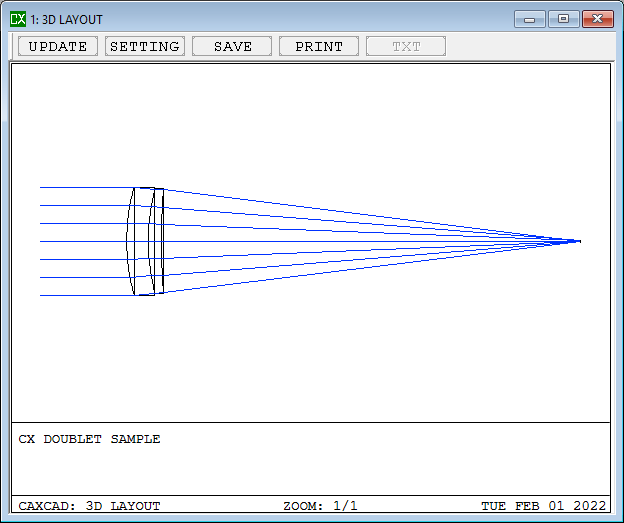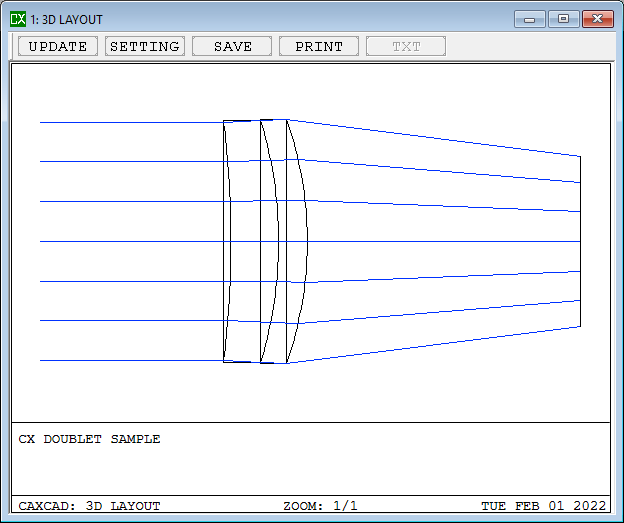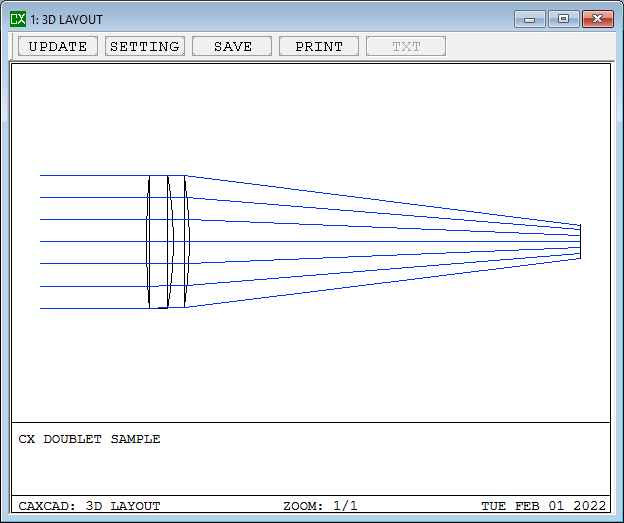
- Details
An aspherical lens is an optical component with a non-spherical surface profile, meaning it deviates from the shape of a perfect sphere. Unlike spherical lenses, which have a constant curvature across their surface, aspherical lenses feature varying curvatures that help correct optical aberrations and improve image quality.

- Details
A singlet refers to a single optical element, typically a lens, that is used in optical systems. Unlike compound lenses, which consist of multiple lens elements, singlets are composed of only one piece of optical material. Singlets are often used in simple optical setups where cost, size, or weight constraints are significant factors, or in applications where aberrations can be effectively controlled using a single optical surface.
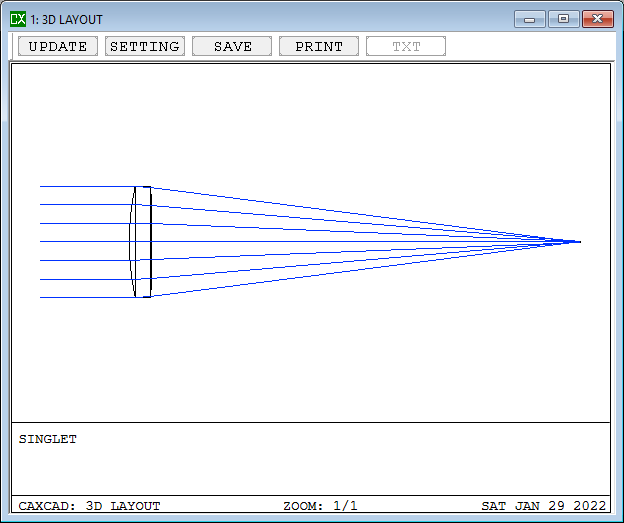
- Details
Infrared thermal imaging lens is an optical lens used for infrared thermal imaging, typically employed to convert infrared radiation into visible images or digital data.
- Details
F-theta (Fθ) scan lens is an optical component commonly used in laser processing applications such as laser cutting, laser marking, and laser engraving.
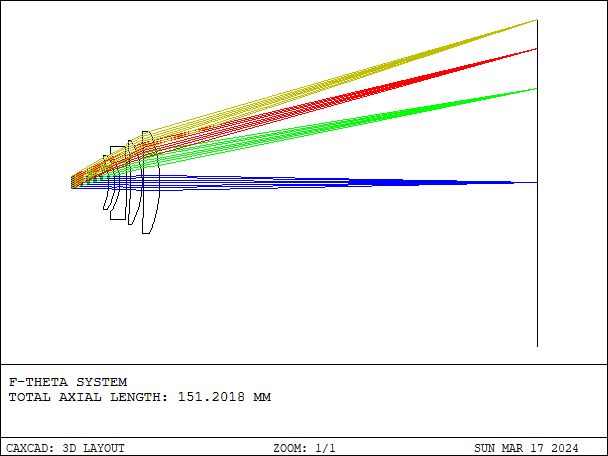
- Details
The Cassegrain Telescope is a type of astronomical telescope design that includes one or more mirror reflectors to collect and focus light, forming an enlarged image. This design is versatile and can achieve various optical performances through different combinations.
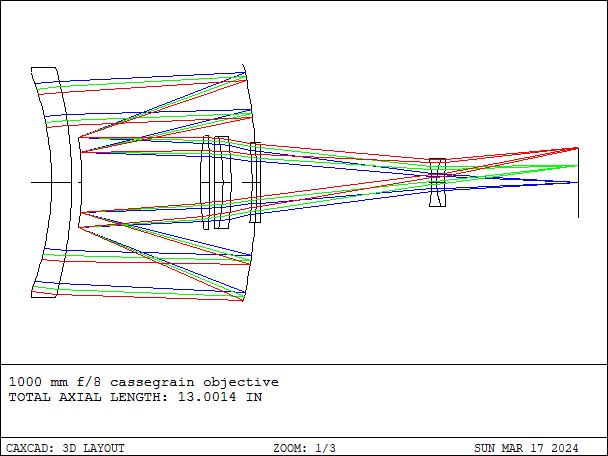
- Details
Endoscope is an optical device used for medical diagnosis and treatment, typically employed to examine the internal organs, tissues, and passages of the human body.
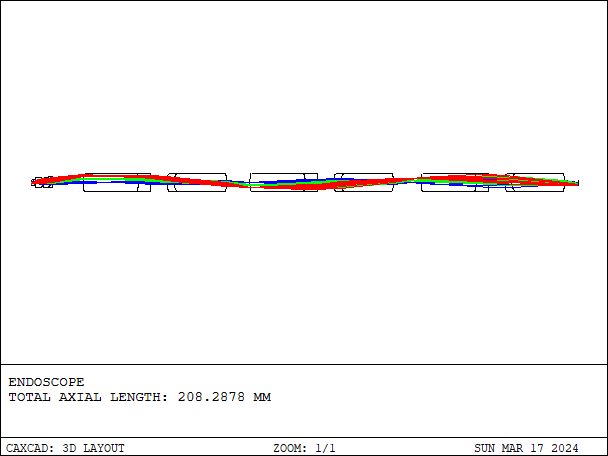
- Details
Relay lens is an optical component used to relay the image from one optical system to another without significantly altering the size or quality of the image. It is commonly employed in various optical setups such as microscopes, cameras, and other imaging systems.
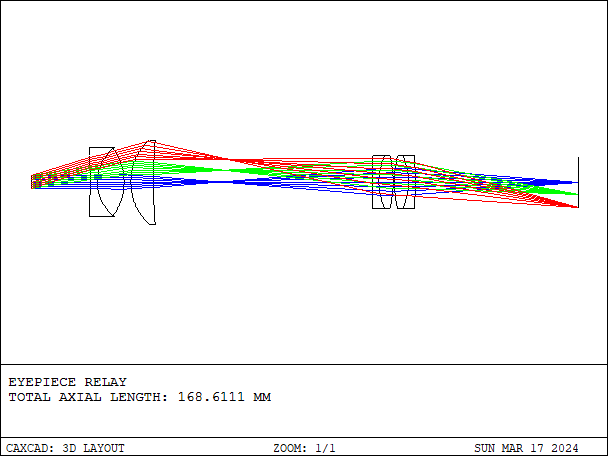
- Details
The Petzval lens is an optical design initially invented by Austrian optical engineer Joseph Petzval in the early 19th century. This lens design holds significant importance in optical history as it was the first successful large-aperture, short focal length lens, contributing significantly to the development of photography technology.
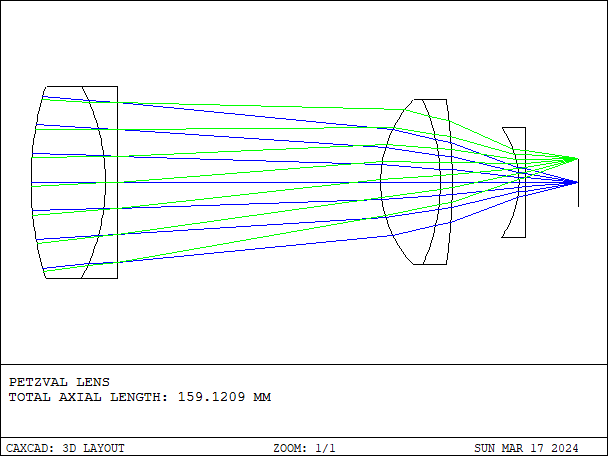
- Details
Wide-angle optical lens design involves many complex optical principles and engineering techniques to ensure clear, high-quality images over a broad field of view. CAXCAD offers rapid wide-angle ray targeting technology, enabling fast design of wide-angle lenses.
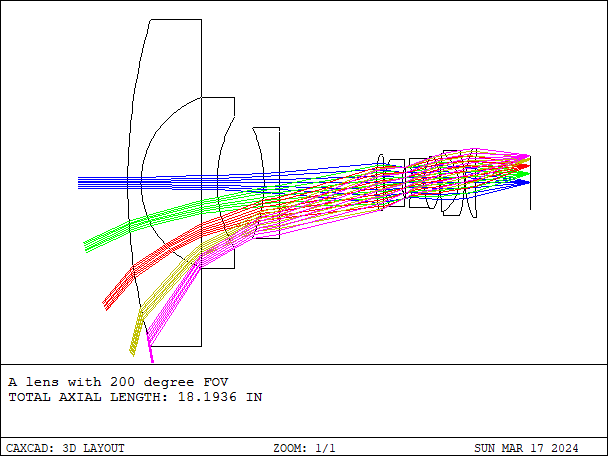
- Details
Telephoto Lens is a specialized type of lens used in photography with the following characteristics:
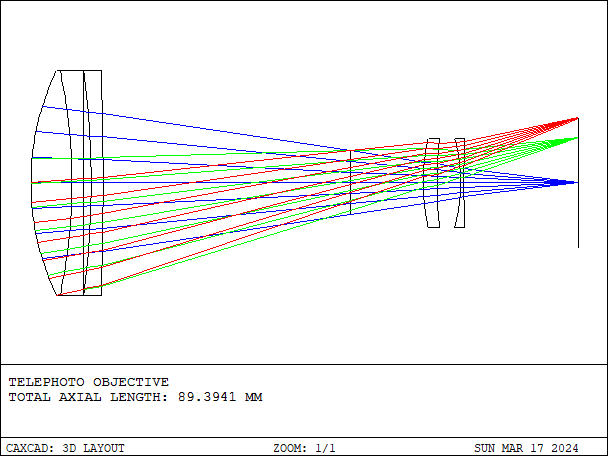
- Details
Imaging objectives are vital components in optical systems, used to convert optical information from the object being imaged into an image. When designing imaging objectives, several factors need to be considered to ensure their performance and quality. Designing imaging objectives using CAXCAD optical design software facilitates a convenient and efficient process!

- Details
Afocal optical system is a specially designed optical system that does not require introducing a focus in the optical system, but achieves the desired optical effects through other means.
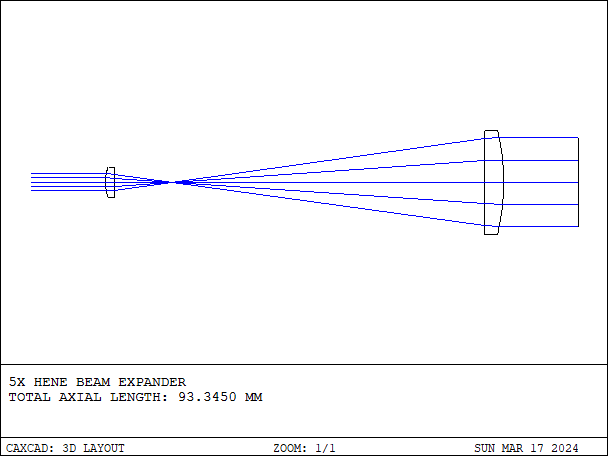
- Details
Eyepiece is an optical device used to observe images or objects in optical instruments. In microscopes and telescopes, eyepieces play a crucial role, each with different designs and functions.
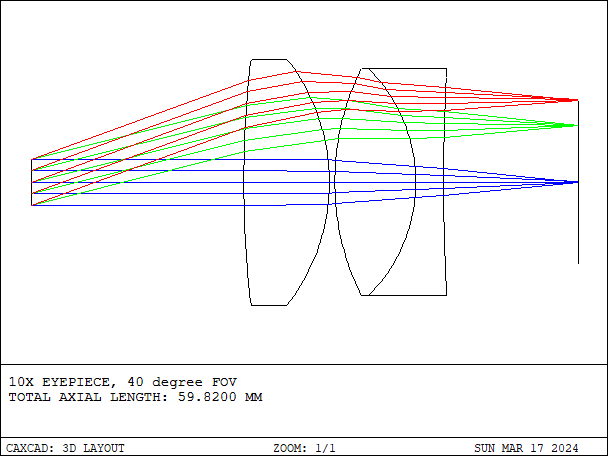
- Details
Binoculars is an optical instrument used for observing distant celestial objects or scenes.
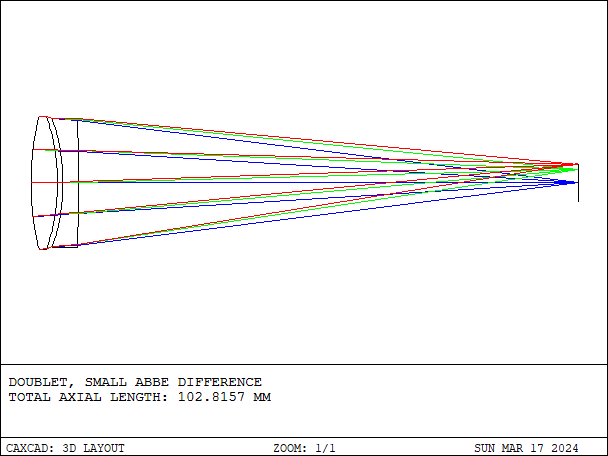
- Details
In camera lens design, three common classic optical configurations include the Double Gauss lens, Cooke lens, and Kodak lens.
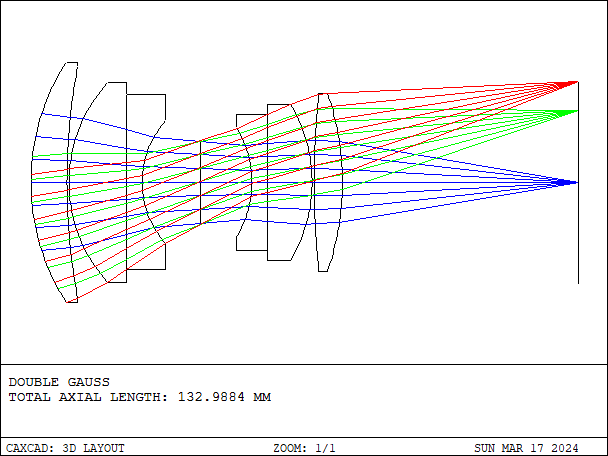
- Details
Microscope objectives are the core components in microscopes, used to magnify and observe tiny objects such as cells and tissues. Designing microscope objectives requires consideration of several factors to ensure their performance and quality.
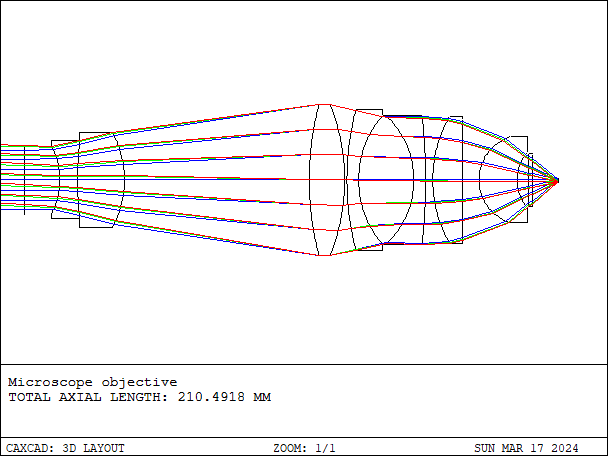
- Details
Introduction
The Optical Path Difference or OPD is core parameter of optical system.
Wavefront Map shows all the OPD distribution.
CAXCAD Provides theWavefront Map Analysis Function as the following introduction.
Graphics Window
CAXCAD uses the exit pupil as the position of reference sphere.

