KNOWLEDGE BASE
- Details
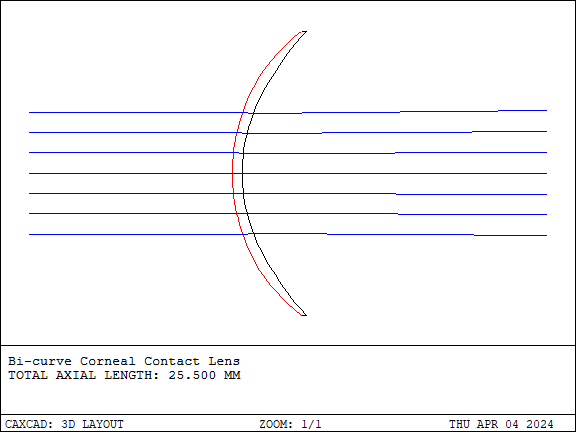
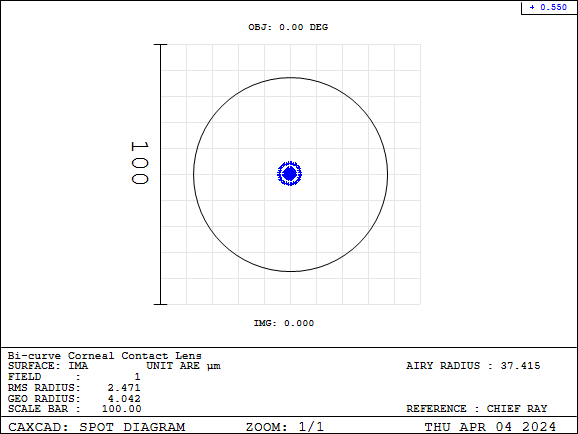
Contact lenses are medical devices used to correct vision, placed directly on the surface of the eye or cornea unlike traditional eyeglasses. They are typically made of soft, breathable materials for comfort and adaptability. Contact lenses can correct vision problems such as nearsightedness, farsightedness, and astigmatism, providing a more natural appearance without obscuring facial features.
 |
 |
- Details
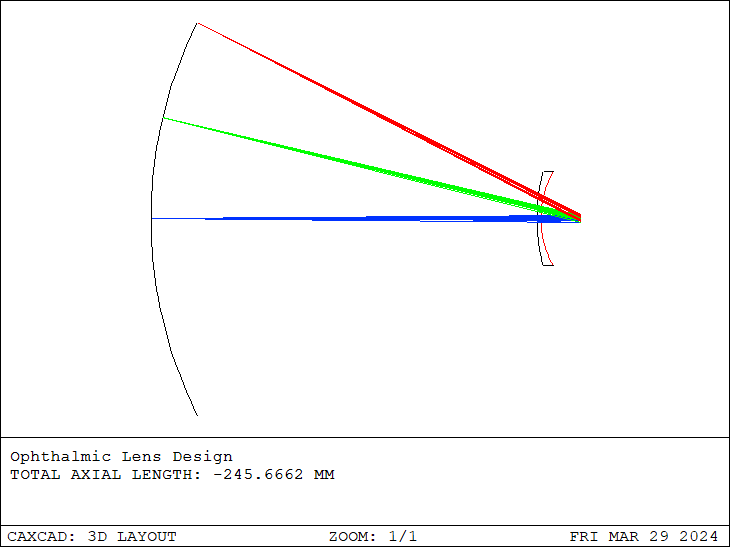
Using CAXCAD for eyeglass lens design is straightforward. Although progressive lens design is not covered in this article, it's worth noting that progressive lenses typically adhere to the basic curve design principles of other eyeglass lenses.
- Details
The human eye is a vital component of the human visual system, responsible for receiving light signals and converting them into visual perception. The human eye consists primarily of the eyeball and the visual nerve. The eyeball includes structures such as the cornea, iris, lens, vitreous humor, and retina.
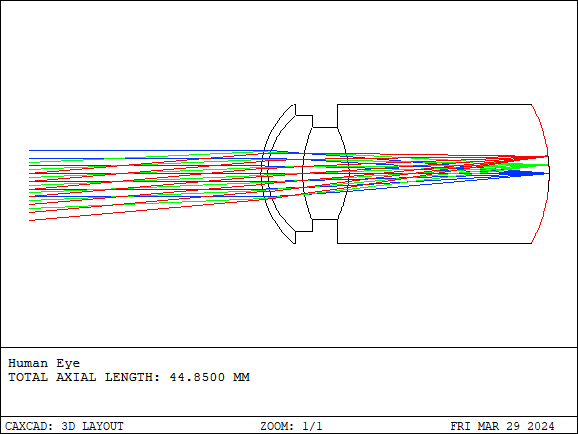
- Details
Ultraviolet lithography lens is an optical component specialized for the lithography process in semiconductor manufacturing.
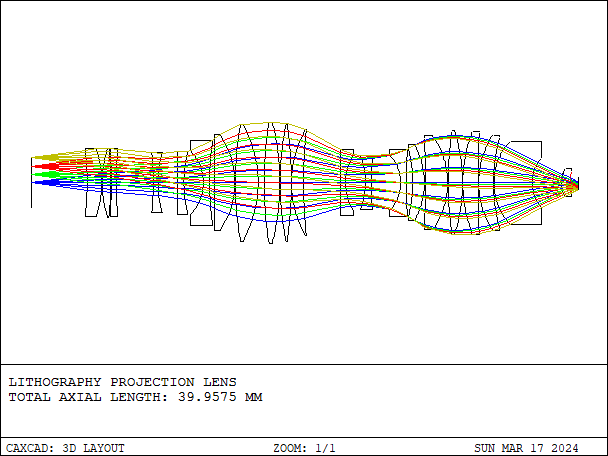
- Details
Ray Aiming is an iterative ray tracing algorithm used in optical design work to find rays in object space that correctly fill the given aperture size. This article will introduce the usage of Ray Aiming and Pupil Aberration in CAXCAD:
- Details
Introduction
The five basic types of aberration which are due to the geometry of lenses or mirrors, and which are applicable to systems dealing with monochromatic light, are known as Seidel aberrations, from an 1857 paper by Ludwig von Seidel. These are the aberrations that become evident in third-order optics, also known as Seidel optics.
SPHA S1,COMA S2, ASTI S3, FCUR S4, DIST S5
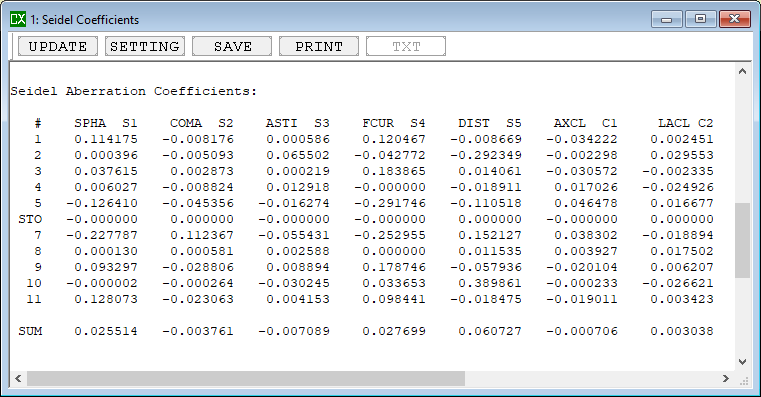
Read more: How to calculate the seidel aberration with CAXCAD ?
- Details
- Most definations are based on the paraxial optics
- The paraxial image height for optical design is fast for calculation, but inaccuracy for wide angle or big distortion
- The real image height needs to calculate the ray iteration and is inaccuracy.
- We wil use a sample in CAXCAD to show the difference
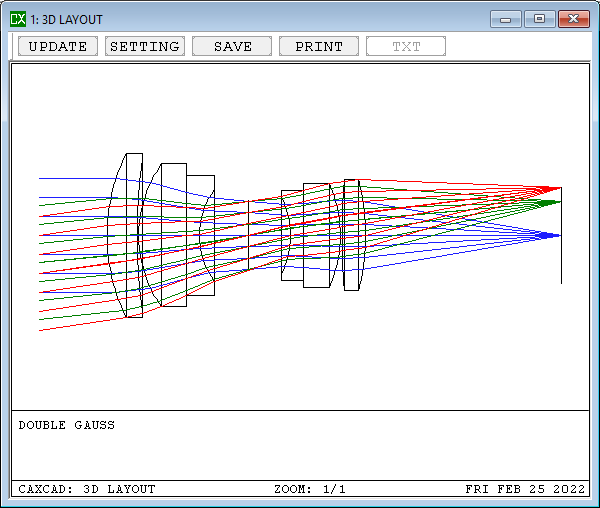
Read more: What is the difference between paraxial and real image height?
- Details
- Multi-Start in DLS Optimization
- Fast Engine in Global Optimization
- Fast Ray Aiming:three modes can be selected and the CX Ray Aiming don't need the iteration of raytracing
- Automatic Design: user don't need to remember the MF operate any more
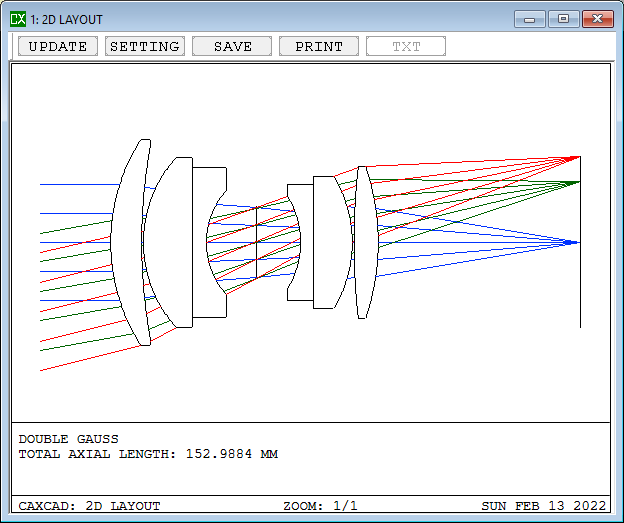
- Details
If this is the first time you have got CAXCAD, please follow this article to install the software. The latest version of the software was named with the date information.
- Details
The first order data is the basic parameters of the lens design. They are from paraxial optics and enable us to compute some of the most basic properties of an optical system with a minimum of calculation.The paraxial treatment can provide the designer with insight into the performance of the system with a modest effort.
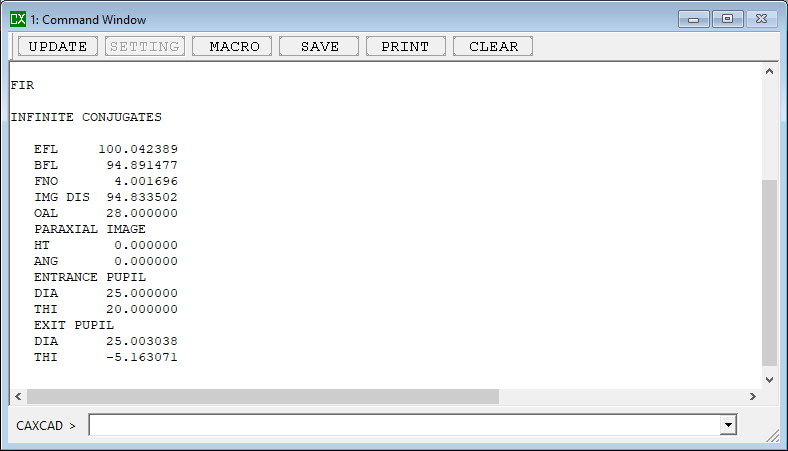
- Details
High yield optimization refers to the process of maximizing the output or productivity of a system, process, or investment while minimizing waste, cost, or resources expended. This concept is commonly applied in various fields, including manufacturing, agriculture, finance, and engineering, among others. The goal of high yield optimization is to achieve the highest possible return or output relative to the resources invested or utilized.
Read more: How to use the High Yield Optimization in CAXCAD?
- Details
Paraxial ray tracing assumes that the tangent and sine of all angles are equal to the angles themselves (in other words, tan(u)=u and sin(u)=u ). This approximation is valid for small angles but can lead to the propagation of error as ray angles increase.
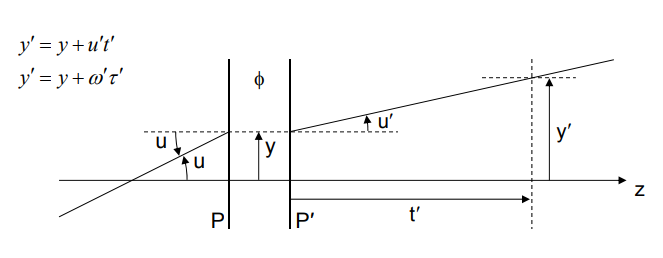
- Details
The Cooke triplet is a photographic lens designed and patented (patent number GB 22,607) in 1893 by Dennis Taylor who was employed as chief engineer by T. Cooke & Sons of York. It was the first lens system that allowed elimination of most of the optical distortion or aberration at the outer edge of lenses. The Cooke triplet is noted for being able to correct the Seidel aberrations.
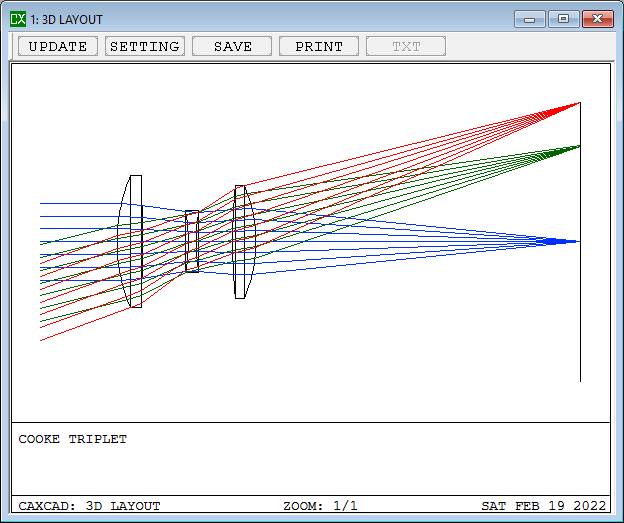
- Details
A doublet is an optical lens assembly consisting of two individual lenses cemented or spaced closely together. The purpose of a doublet is to correct chromatic aberration, a common optical aberration that causes different wavelengths of light to focus at different distances from the lens, resulting in color fringing or blurring in images.
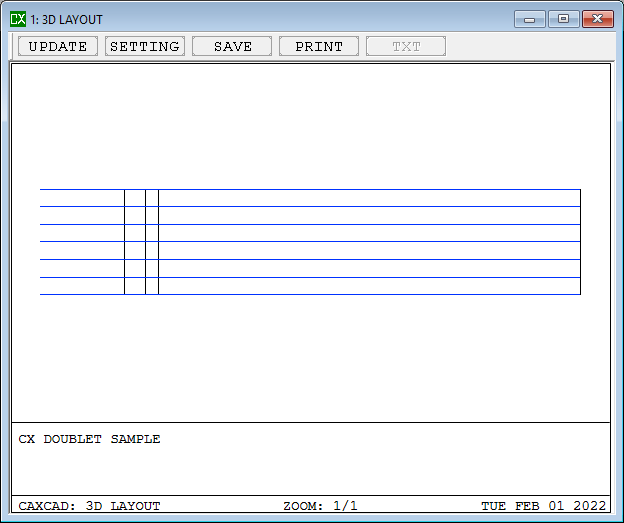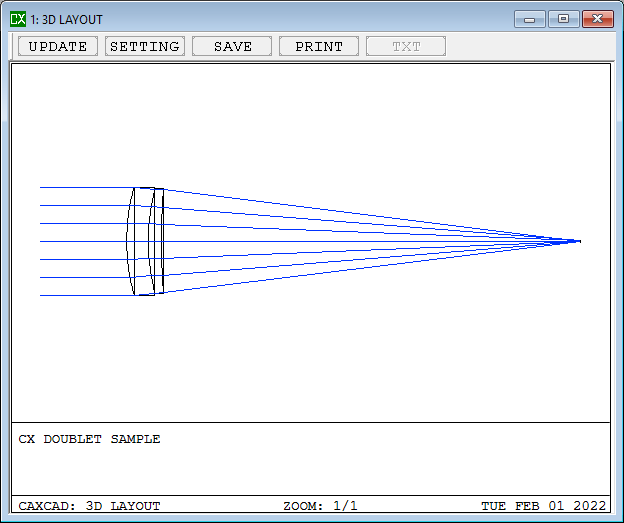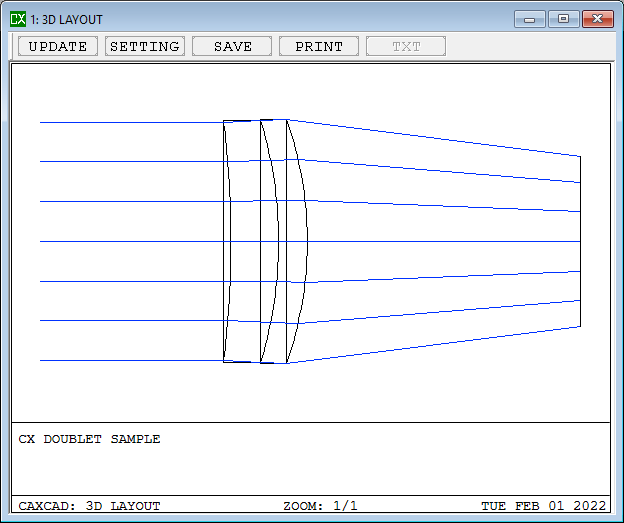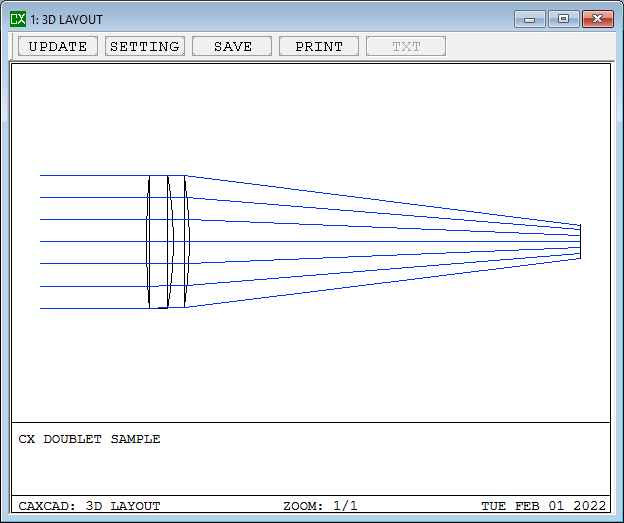
- Details
An aspherical lens is an optical component with a non-spherical surface profile, meaning it deviates from the shape of a perfect sphere. Unlike spherical lenses, which have a constant curvature across their surface, aspherical lenses feature varying curvatures that help correct optical aberrations and improve image quality.

- Details
A singlet refers to a single optical element, typically a lens, that is used in optical systems. Unlike compound lenses, which consist of multiple lens elements, singlets are composed of only one piece of optical material. Singlets are often used in simple optical setups where cost, size, or weight constraints are significant factors, or in applications where aberrations can be effectively controlled using a single optical surface.
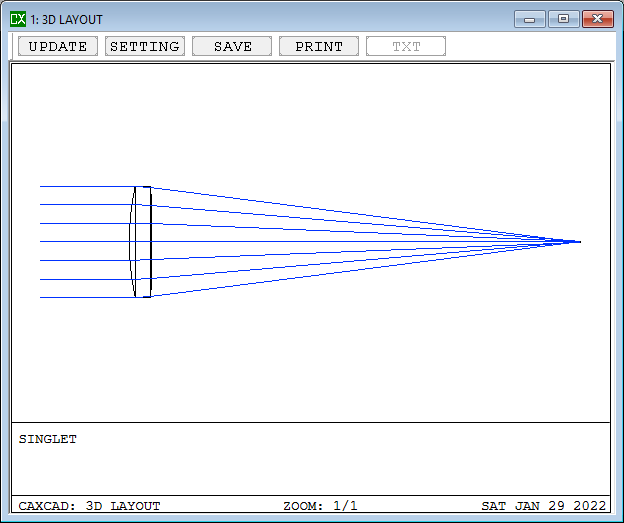
- Details
Infrared thermal imaging lens is an optical lens used for infrared thermal imaging, typically employed to convert infrared radiation into visible images or digital data.
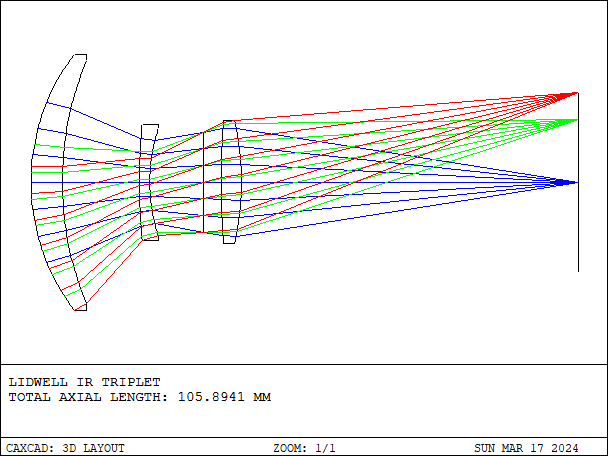
- Details
F-theta (Fθ) scan lens is an optical component commonly used in laser processing applications such as laser cutting, laser marking, and laser engraving.
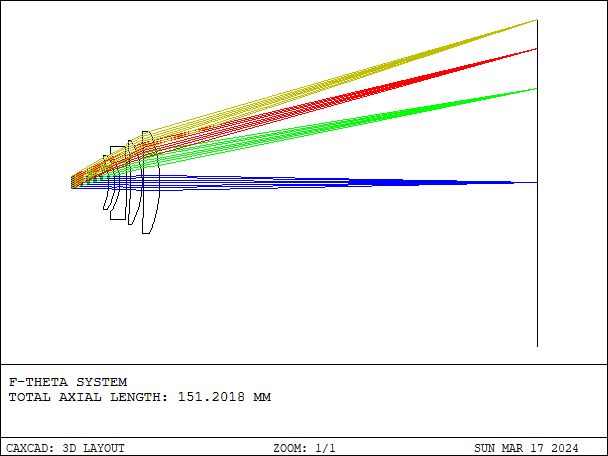
- Details
The Cassegrain Telescope is a type of astronomical telescope design that includes one or more mirror reflectors to collect and focus light, forming an enlarged image. This design is versatile and can achieve various optical performances through different combinations.
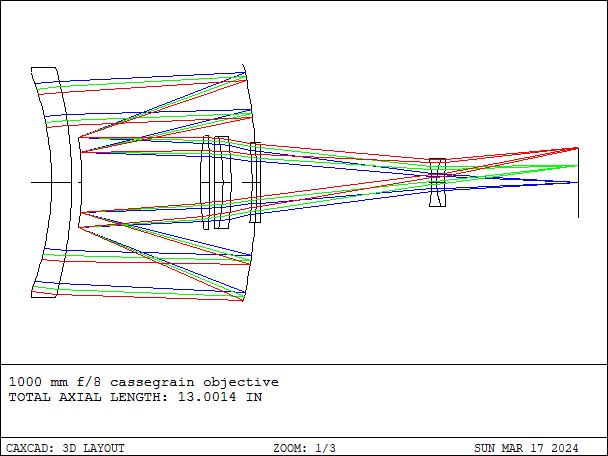
- Details
Endoscope is an optical device used for medical diagnosis and treatment, typically employed to examine the internal organs, tissues, and passages of the human body.
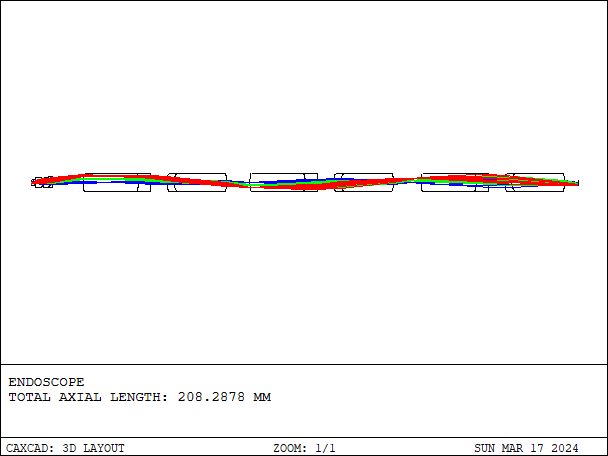
- Details
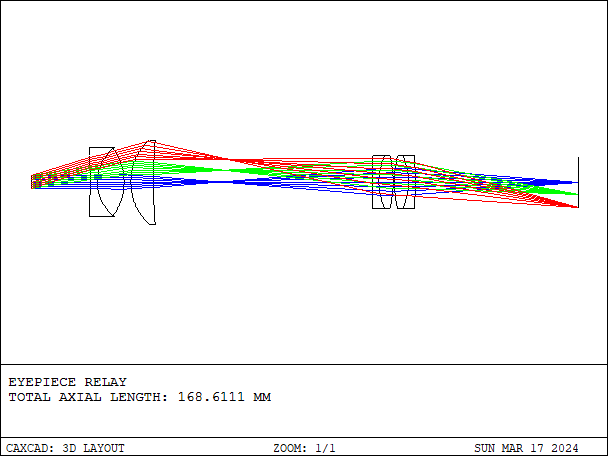
Relay lens is an optical component used to relay the image from one optical system to another without significantly altering the size or quality of the image. It is commonly employed in various optical setups such as microscopes, cameras, and other imaging systems.